Spatial
domain (Image Enhancement)
Definition
-
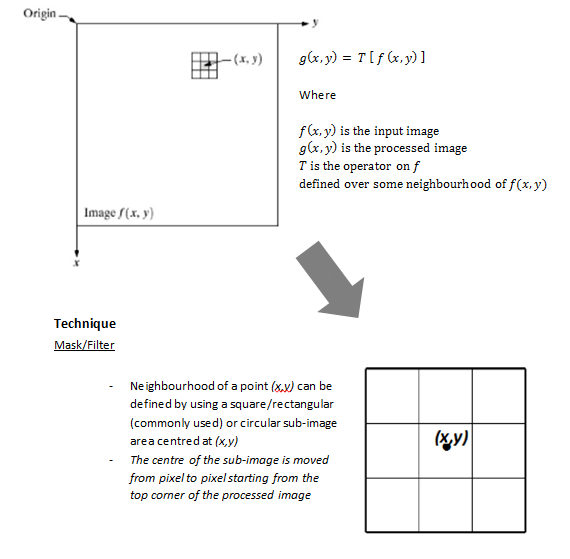
Techniques are based on direct manipulation of
pixels in an image
-
“normal” image space
-
Changes in pixel positions correspond to changes
in the scene
-
Distances in / correspond to real distances
-
Directly process the input image pixel array
-
An image processing operation transform
the gray value of the pixels
-
In order to perform the transformation,
the image must undergo 3 process
i.
Point
processing -
Gray values change without any knowledge of its surrounding
ii.
Neighbourhood
processing – Gray values change depends on the gray
value in a small neighbourhood of pixels around the given pixel.
iii.
Transform
– Gray values are represented in a different domain but
equivalent form; Fourier, wavelet.
Point processing
·
Neighbourhood = 1*1 pixel
·
g depends on only the value of f at (x,y)
· T = gray level (or intensity or mapping)
transformation function
s = T(r)
where
r
= gray level of f(x,y)
s
=gray level of g(x,y)
Arithmetic
Operation
·
Act by applying a simple arithmetic
functions
s = T(r)
to
each gray level in the image
·
T is a function that maps r to s.
·
Additions, subtraction, scaling (multiplication
& division), complement
Image Subtraction
g(x,y) = f(x,y) - h(x,y)
- Is obtained by computing the difference between all pairs of corresponding pixels
- Usefulness: enhancement of differences between images
Image
Negatives
The appearance of photographic negatives
- It enhances white or gray detail on dark regions especially when black areas are dominant in size.
Identity function
- what “goes in” , “comes out” the same
Log transformation
- bring up the details that are not visible due to large dynamic range of values
Inverse Log
Transformation
- the opposite of Log transformation
- used to expand the higher value pixels in an image while compressing darker-level values.
Power-Law
Transformation
Gamma Correction
- make linear input appear linear on displays
- method: calibration pattern + interactive adjustment
-
- effect gamma on consumer photos










No comments:
Post a Comment